Answer:
In a quadratic equation of the shape:
y = a*x^2 + b*x + c
we hate that the discriminant is equal to:
D = b^2 - 4*a*c
This thing appears in the Bhaskara's formula for the roots of the quadratic equation:
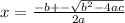
You can see that the determinant is inside a square root, this means that if D is smaller than zero we will have imaginary roots (the graph never touches the x-axis)
If D = 0, the square root term dissapear, and this implies that both roots of the equation are the same, this means that the graph touches the x axis in only one point, wich coincides with the minimum/maximum of the graph)
If D > 0 we have two different roots, so the graph touches the x-axis in two different points.