Answer:
Approximately
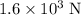 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
By the Impulse-Momentum Theorem, the change in this woman's momentum will be equal to the impulse that is applied to her.
The momentum
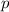 of an object is equal to the product of its mass
of an object is equal to the product of its mass
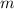 and velocity
and velocity
 . That is:
. That is:
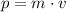 .
.
Let
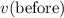 and
and
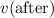 represent the velocity of the woman before and after the landing. Let
represent the velocity of the woman before and after the landing. Let
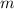 represent the woman's mass.
represent the woman's mass.
- The woman's momentum before the landing would be
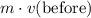 .
. - The woman's momentum after the landing would be
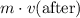 .
.
Therefore, the change in this woman's momentum would be:
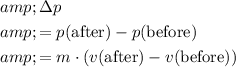 .
.
On the other hand, impulse is equal to force multiplied by the duration of the force. Let
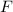 represent the average force on the woman. The impulse on her during the landing would be
represent the average force on the woman. The impulse on her during the landing would be
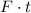 .
.
Apply the Impulse-Momentum Theorem.
- Impulse:
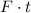 .
. - Change in momentum:
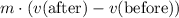 .
.
Impulse is equal to the change in momentum:
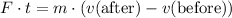 .
.
After landing, the woman comes to a stop. Her velocity would become zero. Therefore,
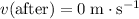 .
.
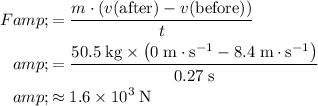 .
.