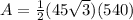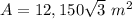Answer:
Part 1) Triangle:
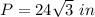 and
and
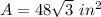
Part 2) Square:
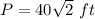 and
and
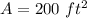
Part 3) Hexagon 1:
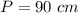 and
and
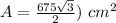
Part 4) Hexagon 2:
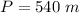 and
and
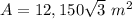
Explanation:
Part 1) we have an equilateral triangle
we know that
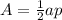
where
a is the apothem
P is the perimeter
step 1
Find the length side of the equilateral triangle
Let
b ----> the length side of triangle
we know that
The measure of each interior angle is 60 degrees
so
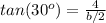 ---> by TOA (opposite side divided by the adjacent side)
---> by TOA (opposite side divided by the adjacent side)
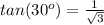
equate
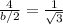
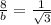
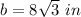
step 2
Find the perimeter
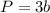
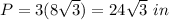
step 3
Find the area
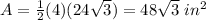
Part 2) we have a square
we know that
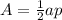
where
a is the apothem
P is the perimeter
step 1
Find the length side of the square
Let
b ----> the length side of the square
we know that
The diagonal is half the radius of the square
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
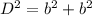
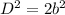
we have
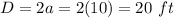
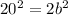
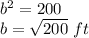
simplify
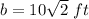
step 2
Find the perimeter
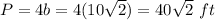
step 3
Find the area
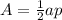
The apothem is half the length side of the square
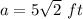
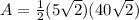
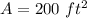
Part 3) we have a regular hexagon
we know that
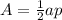
where
a is the apothem
P is the perimeter
step 1
Find the length side of the hexagon
we know that
The length side of a regular hexagon is equal to the radius
Let
b ----> the length side of the hexagon
we have
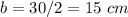 ----> the radius is half the diameter
----> the radius is half the diameter
step 2
Find the perimeter
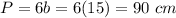
step 3
Find the area
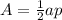
The apothem is the height of an equilateral triangle
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
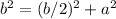
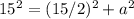
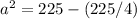
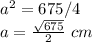
simplify
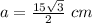
substitute in the formula of area
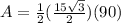
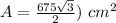
Part 4) we have a regular hexagon
we know that
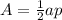
where
a is the apothem
P is the perimeter
step 1
Let
b ---> the length side of the hexagon
we have
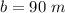
Find the perimeter
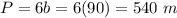
step 2
Find the area
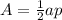
The apothem is the height of an equilateral triangle
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
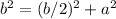
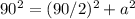
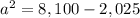
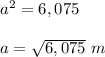
simplify
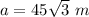
substitute in the formula of area