Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
You can use the combined gas law:
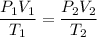
You need to find P₂ when:
- T₁ = - 13.0 + 273.15 K = 260.15 K
- T₂ = 17.0 + 273.15 K = 290.15 K
Thus, clear P₂ from the equation, subsitute and compute:
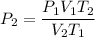
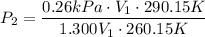
P₂ = 0.26kPa ← answer
Since the factor P₁ has two significant figures, the result is limited to two significant figures.