Answer:
1.6 moles of iron
Step-by-step explanation:
-Metals reacts with oxygen to form oxides.
-The chemical reaction between oxygen and iron is written as below:
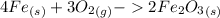
-pu notice from the balanced chemiocal equation above that the mole ration of iron to oxygen is 4:3
-We equate and cross multiply to find moles of iron in the reaction;
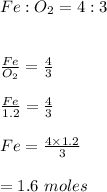
Hence, 1.6 moles of iron reacts with 1.2 moles of oxygen in the above reaction.