Answer : The pressure of carbon dioxide in the reaction vessel after the reaction is, 0.59 atm.
Explanation : Given,
Mass of
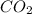 = 12 g
= 12 g
Molar mass of
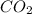 = 44 g/mol
= 44 g/mol
First we have to calculate the moles of carbon dioxide gas.
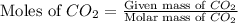
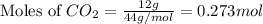
Now we have to calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
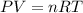
where,
P = pressure of gas = ?
V = volume of gas = 10.0 L
n = number moles of gas = 0.273 mol
R = gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol.K
T = temperature of gas =
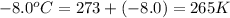
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
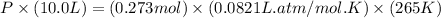
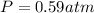
Therefore, the pressure of carbon dioxide in the reaction vessel after the reaction is, 0.59 atm.