Noticing that there is a pattern of repetition in the question (the numbers are repeated twice), we are assuming that the mean number of words per minute is 88, the standard deviation is of 14 WPM, as well as the number of sixth graders is 137, and that there is a need to estimate the probability that the sample mean would be greater than 89.87.
Answer:
"The probability that the sample mean would be greater than 89.87 WPM" is about
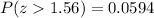 .
.
Explanation:
This is a problem of the distribution of sample means. Roughly speaking, we have the probability distribution of samples obtained from the same population. Each sample mean is an estimation of the population mean, and we know that this distribution behaves normally for samples sizes equal or greater than 30
 . Mathematically
. Mathematically
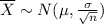 [1]
[1]
In words, the latter distribution has a mean that equals the population mean, and a standard deviation that also equals the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size.
Moreover, we know that the variable Z follows a normal standard distribution, i.e., a normal distribution that has a population mean
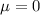 and a population standard deviation
and a population standard deviation
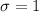 .
.
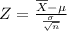 [2]
[2]
From the question, we know that
- The population mean is
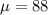 WPM
WPM - The population standard deviation is
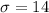 WPM
WPM
We also know the size of the sample for this case:
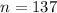 sixth graders.
sixth graders.
We need to estimate the probability that a sample mean being greater than
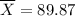 WPM in the distribution of sample means. We can use the formula [2] to find this question.
WPM in the distribution of sample means. We can use the formula [2] to find this question.
The probability that the sample mean would be greater than 89.87 WPM
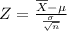
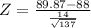
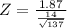
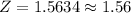
This is a standardized value and it tells us that the sample with mean 89.87 is 1.56 standard deviations above the mean of the sampling distribution.
We can consult the probability of P(z<1.56) in any cumulative standard normal table available in Statistics books or on the Internet. Of course, this probability is the same that
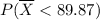 . Then
. Then
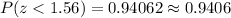
However, we are looking for P(z>1.56), which is the complement probability of the previous probability. Therefore
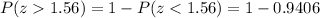
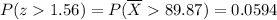
Thus, "The probability that the sample mean would be greater than 89.87 WPM" is about
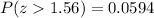 .
.