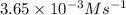Answer : The rate constant for this reaction is,
Explanation :
To calculate the rate constant for zero order reaction, the expression used is:
![\ln [A]=-kt+\ln [A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6l40dplqu001moxruhc0fyzghv8i0an9sp.png)
where,
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/3jrctnxyrdjmiz9ngr0s6o9r3hdvpo6qhe.png) = initial concentration
= initial concentration
![[A]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3c3qqp51mqk0xw1nmfldczp98fmi09kbrv.png) = final concentration =
= final concentration =
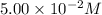 at 195 s
at 195 s
![[A]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3c3qqp51mqk0xw1nmfldczp98fmi09kbrv.png) = final concentration =
= final concentration =
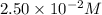 at 385 s
at 385 s
k = rate constant = ?
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
![\ln (5.00* 10^(-2))=-k* 195+\ln [A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qrt4moolwr81fylplyi2zjgp7zyrff5r7c.png) ............(1)
............(1)
and,
![\ln (2.50* 10^(-2))=-k* 385+\ln [A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/54g1xlbilvbckynvrcrkwgqan5sxziyn5i.png) ............(2)
............(2)
Subtracting 1 from 2, we get:
![\ln (2.50* 10^(-2))-\ln (5.00* 10^(-2))=-k* 385+\ln [A_o]+k* 195-\ln [A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wnvzo0j16pxquo673alq622x97ubsffwcv.png)
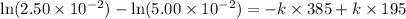
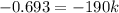
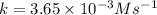
Therefore, the rate constant for this reaction is,