Answer:
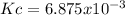
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given chemical reaction at equilibrium:
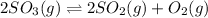
The initial concentration of sulfur trioxide is:
![[SO_3]_0=(0.660mol)/(4.00L)=0.165M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/iu18iyxiatti3x49aolp9fziwk3pmxpgxo.png)
Hence, the law of mass action to compute Kc results:
![Kc=([SO_2]^2[O_2])/([SO_3]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ldlut11lzz144c8zg937nejktb3owrq9fq.png)
In such a way, in terms of the change
 due to the reaction extent, by using the ICE method, it is modified as:
due to the reaction extent, by using the ICE method, it is modified as:
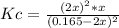
In that case, as at equilibrium 0.11 moles of oxygen are present,
 equals:
equals:
![x=[O_2]=(0.110mol)/(4.00L)=0.0275M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6i7wmwal54cd2sls6tx2hfi34clwwtelrc.png)
Therefore, the equilibrium constant finally turns out:

Best regards.