Answer:
Type II error
Explanation:
Type 1 error occurs when:
We reject a True Null Hypothesis
Type 2 error occurs when:
We fail to reject a wrong Null Hypothesis.
The given hypothesis are:
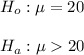
Level of significance = α = 0.05
The calculated z test statistic = z = 1.47
In order to make a decision we first need to convert z = 1.47 to its equivalent p-value. From the z-table the p value for z score being greater than 1.47 comes out to be:
p-value = 0.0708
Since, p-value is greater than the level of significance, we fail to reject the Null Hypothesis.
It is given that the true value of μ is 25. If the true value of μ is 25, then the Null hypothesis was false. But from the test we performed, we failed to reject the Null Hypothesis.
Since, we failed to reject a False Null Hypothesis, the conclusion resulted in a Type II error.