Answer:
Check the explanation
Step-by-step explanation:
Answer – Given,
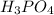 acid and there are three Ka values
acid and there are three Ka values
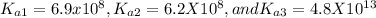
The transformation of
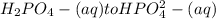 is the second dissociation, so we need to use the Ka2 = 6.2x10-8 in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
is the second dissociation, so we need to use the Ka2 = 6.2x10-8 in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Mass of KH2PO4 = 22.0 g , mass of Na2HPO4 = 32.0 g , volume = 1.00 L
First we need to calculate moles of each
Moles of KH2PO4 = 22.0 g / 136.08 g.mol-1
= 0.162 moles
Moles of Na2HPO4 = 32.0 g /141.96 g.mol-1
= 0.225 moles
[H2PO4-] = 0.162 moles / 1.00 L = 0.162 M
[HPO42-] = 0.225 moles / 1.00 L = 0.225 M
Now we need to calculate the pKa2
pKa2 = -log Ka
= -log 6.2x10-8
= 7.21
We know Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [conjugate base] / [acid]
pH = 7.21 + log 0.225 / 0.162
= 7.35
The pH of a buffer solution obtained by dissolving 22.0 g of KH2PO4 and 32.0 g of Na2HPO4 in water and then diluting to 1.00 L is 7.35