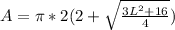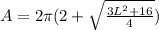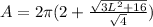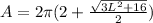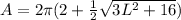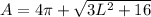Answer:
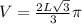
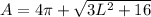
Explanation:
Figure of cone is missing. See attachment
Given
Radius, R = 2m
Let L = KL=LM=KM
Required:
Volume, V and Surface Area, A
Calculating Volume
Volume is calculated using the following formula
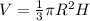
Where R is the radius of the cone and H is the height
First, we need to determine the height of the cone
The height is represented by length OL
It is given that KL=LM=KM in triangle KLM
This means that this triangle is an equilateral triangle
where OM = OK =
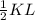
OK =
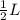
Applying pythagoras theorem in triangle LOM,
|LM|² = |OL|² + |OM|²
By substitution
L² = H² + (
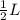 )²
)²
H² = L² -
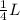 ²
²
H² = L² (1 -
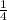 )
)
H² = L²
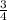
H² =
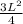
Take square root of bot sides
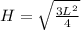
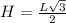
Recall that
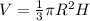
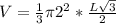

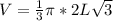
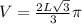
in terms of
 an d L where L = KL = LM = KM
an d L where L = KL = LM = KM
Calculating Surface Area
Surface Area is calculated using the following formula
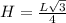
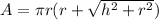
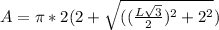 )
)
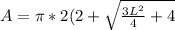 )
)