Answer:
Limiting reactant: Oxygen
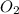
Step-by-step explanation:
First write the balanced chemical equation:
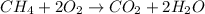
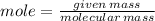
given mass of methane =25g
molecular mass of methane=16g/mol
mole=1.5625mol
given mass of oxygen=50
molar mass of oxygen=32g/mol
mole=1.5625mol
from the above balanced equation it is clearly that,
1 mole of methane needs 2 moles of oxygen for complete reaction
Therefore,
1.5625 moles of methane needs 3.125 moles of oxygen for complete reaction but we have only 1.5625 moles of oxygen,
hence,
oxygen will be the limiting reactant and methane will be the excess reactant