Answer:
The statistic is z=-0.674.
The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.
Explanation:
To make conclusions about the effectiveness of the new method, they should perform an hypothesis test on the proportion of failed cancer detection.
The actual method has a proportion of failed cancer detection of p=0.15. If the new method is better, it should have enough evidence that its actual proportion is below 0.15. This claim, that the new method proportion is below 0.15, will be stated in the alternative hypothesis.
The null and alternative hypothesis are:
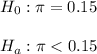
The sample size is n=70.
The sample proportion is p=8/70=0.114.
The standard error is calculated as:
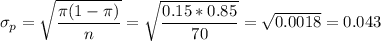
Then, the z-statistic for this sample is:
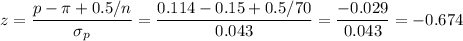
The P-value for this statistic is:
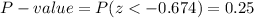
At a significance level of 0.1, the P-value is bigger, so the effect is not significant. The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.