Answer:
Probability that the sample mean comprehensive strength exceeds 4985 psi is 0.99999.
Explanation:
We are given that a random sample of n = 9 structural elements is tested for comprehensive strength. We know the true mean comprehensive strength μ = 5500 psi and the standard deviation is σ = 100 psi.
Let
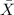 = sample mean comprehensive strength
= sample mean comprehensive strength
The z-score probability distribution for sample mean is given by;
Z =
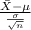 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
 = population mean comprehensive strength = 5500 psi
= population mean comprehensive strength = 5500 psi
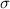 = standard deviation = 100 psi
= standard deviation = 100 psi
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is away from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value (area) associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X.
Now, Probability that the sample mean comprehensive strength exceeds 4985 psi is given by = P(
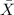 > 4985 psi)
> 4985 psi)
P(
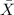 > 4985 psi) = P(
> 4985 psi) = P(
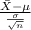 >
>
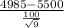 ) = P(Z > -15.45) = P(Z < 15.45)
) = P(Z > -15.45) = P(Z < 15.45)
= 0.99999
Since in the z table the highest critical value of x for which a probability area is given is x = 4.40 which is 0.99999, so we assume that our required probability will be equal to 0.99999.