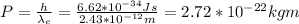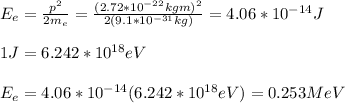Answer:
a) 4.04*10^-12m
b) 0.0209nm
c) 0.253MeV
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula for Compton's scattering is given by:
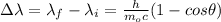
where h is the Planck's constant, m is the mass of the electron and c is the speed of light.
a) by replacing in the formula you obtain the Compton shift:
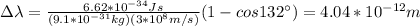
b) The change in photon energy is given by:
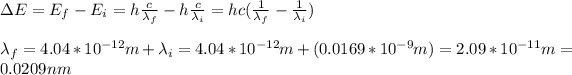
c) The electron Compton wavelength is 2.43 × 10-12 m. Hence you can use the Broglie's relation to compute the momentum of the electron and then the kinetic energy.