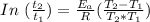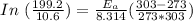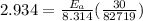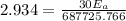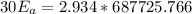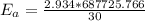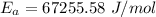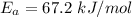Answer:
1. 67.2 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the derived expression from Arrhenius Equation
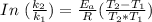
Given that:
time
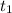 = 8.3 days = (8.3 × 24 ) hours = 199.2 hours
= 8.3 days = (8.3 × 24 ) hours = 199.2 hours
time
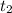 = 10.6 hours
= 10.6 hours
Temperature
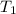 = 0° C = (0+273 )K = 273 K
= 0° C = (0+273 )K = 273 K
Temperature
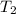 = 30° C = (30+ 273) = 303 K
= 30° C = (30+ 273) = 303 K
Rate = 8.314 J / mol
Since
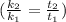
Then we can rewrite the above expression as: