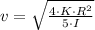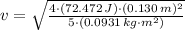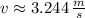Answer:
a)
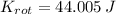 , b)
, b)
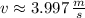 , c)
, c)
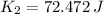 , d)
, d)
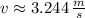
Step-by-step explanation:
b) The kinetic energy for a rigid body is the sum of translational and rotational kinetic energy:
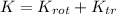
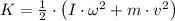
![K = (1)/(2)\cdot \left[I\cdot \left((v)/(R) \right)^(2) +m\cdot v^(2)\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/14p3nu7nr8fxxwr4auvcqcfda8j079z5so.png)
![K = (1)/(2)\cdot \left[(I)/(R^(2))+(3\cdot I)/(2\cdot R^(2)) \right] \cdot v^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/m0uo7kj50mawtkblvxlzajbfco9op2nhpm.png)
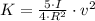
The speed of the center of mass of the sphere at the initial position is:
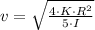
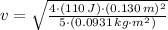
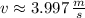
a) The kinetic energy associated with the rotation is:
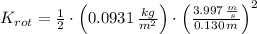
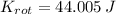
It is 40 % of the total initial kinetic energy.
c) The total final kinetic energy is:
![K_(2) = 110\,J - \left[(3\cdot \left(0.0931\,kg\cdot m^(2)\right))/(2\cdot (0.130\,m)^(2)) \right]\cdot \left(9.807\,(m)/(s^(2)) \right)\cdot (1.20\,m)\cdot \sin 22.7^(\textdegree)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/3vckpr8g9noyl7q3zzc7nzgnj36cm9yr42.png)
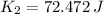
d) The speed of its center of mass is: