Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
The objective of these surveys is to compare if the population variances of the studying hours of econ students and poly sci students are equal.
To do this analysis you have to conduct a variance ratio test.
Be:
X₁: Time in hours that an economy students studies
n₁: 21 students
X[bar]₁= 25 hs
S₁²= 36 hs
And
X₂: Time in hours that a poly sciences students studies
n₂: 16 students
X[bar]₂= 7 hs
S₂²= 85 hs
The hypotheses are:
H₀: σ₁² = σ₂²
H₁: σ₁² ≠ σ₂²
α: 0.01
The test statistic is a Snedecor's F
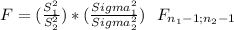
This test is two-tailed so the rejection region is divided in two tails:
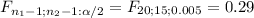
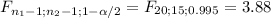
So, you will reject the null hypothesis if
 ≤ 0.29 or if
≤ 0.29 or if
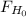 ≥ 3.88
≥ 3.88
And you will not reject the null hypothesis if 0.29 <
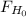 < 3.88
< 3.88
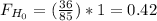
This value is between 0.29 and 3.88, then the decision is to not reject the null hypothesis.
Using a 1% level of significance, there is no significant evidence to reject the null hypothesis. You can conclude that the population variances of the time the economy and poly science students spend studying are the same.
I hope this helps!