Answer:
Hypothesis test on a proportion.
There is no enough evidence to support the claim that the proportion of business executives in the sample differs from the national magazine poll.
Explanation:
We should test the hypothesis of the proportion, with a z-statistic.
The claim is that the proportion of business executives in the sample differs from the national magazine poll.
Then, the null and alternative hypothesis are:
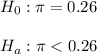
The significance level is assumed to be 0.05.
The sample, of size n=100, has a proportion p=0.19.
The standard error for the proportion is:
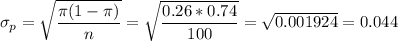
Then, the z-statistic can be calculated as:
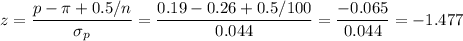
The P-value for this one-tailed test is:
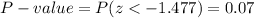
As the P-value is bigger than the significance level, the effect is not significant. The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.
There is no enough evidence to support the claim that the proportion of business executives in the sample differs from the national magazine poll.