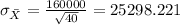Answer:
From the central limit theorem we know that the distribution for the sample mean
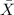 is given by:
is given by:
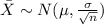
The mean would be:
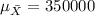
And the standard deviation would be:
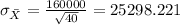
Explanation:
Previous concepts
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
The Z-score is "a numerical measurement used in statistics of a value's relationship to the mean (average) of a group of values, measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean".
Solution to the problem
Let X the random variable that represent the selling price of a population, and for this case we know the following info
Where
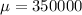 and
and
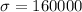
The central limit theorem states that "if we have a population with mean μ and standard deviation σ and take sufficiently large random samples from the population with replacement, then the distribution of the sample means will be approximately normally distributed. This will hold true regardless of whether the source population is normal or skewed, provided the sample size is sufficiently large".
From the central limit theorem we know that the distribution for the sample mean
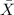 is given by:
is given by:
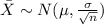
The mean would be:
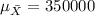
And the standard deviation would be: