Answer:
1. In general, the percentage of ESU students who wear school clothing is the same as that of MSU students.
2. In general, the percentage of ESU students who wear school clothing is different from that of MSU students.
3. Difference between proportions = 0.08
4. Sample size in each group
5. Large
6. Small
Explanation:
1. The null hypothesis usually express that there is no difference between certain characteristics of the populations.
In this case it would state that the proportions are the same for ESU and MSU.
The appropiate null hypothesis is:
In general, the percentage of ESU students who wear school clothing is the same as that of MSU students.
2. The alternative hypothesis express the claim that we are trying to test. In this case, that the proportion differs between ESU and MSU.
The appropiate alternative hypothesis is:
In general, the percentage of ESU students who wear school clothing is different from that of MSU students.
3. The only statistic that can be calculated is the difference between proportions:
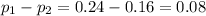
4. We need the sample size of each of both samples (ESU and MSU) in order to calculate the standard error.
Sample size in each group
5. The statistic z is calculated as the division of the difference of proportions, that will remain constant independent of the sample size, and the standard error, that depends on the sample size.
The standard error decreases with an increasing sample size. If the standard error decreases, the z-statistic increases, leading to a most extreme value that will eventually be statistically significant.
Then, a sufficiently large sample will lead to a difference that is statistically significant.
The right answer is:
large
6. Applying the same analysis as in point 5, only if the sample is small, the different would be not statistically significant.
The right answer is:
small