Answer:
(a) We reject our null hypothesis.
(b) We fail to reject our null hypothesis.
(c) We fail to reject our null hypothesis.
Explanation:
We are given that a certain pen has been designed so that true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions (involving the use of a writing machine) is at least 10 hr.
A random sample of 18 pens is selected.
Let
 = true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions
= true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions
So, Null Hypothesis,
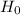 :
:
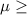 10 hr {means that the true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions is at least 10 hr}
10 hr {means that the true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions is at least 10 hr}
Alternate Hypothesis,
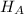 :
:
 < 10 hr {means that the true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions is less than 10 hr}
< 10 hr {means that the true average writing lifetime under controlled conditions is less than 10 hr}
The test statistics that is used here is one-sample t test statistics;
T.S. =
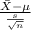 ~
~
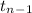
where,
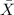 = sample mean
= sample mean
s = sample standard deviation
n = sample size of pens = 18
n - 1 = degree of freedom = 18 -1 = 17
Now, the decision rule based on the critical value of t is given by;
- If the value of test statistics is more than the critical value of t at 17 degree of freedom for left-tailed test, then we will not reject our null hypothesis as it will not fall in the rejection region.
- If the value of test statistics is less than the critical value of t at 17 degree of freedom for left-tailed test, then we will reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region.
(a) Here, test statistics, t = -2.4 and level of significance is 0.05.
Now, at 0.05 significance level, the t table gives critical value of -1.74 at 17 degree of freedom.
Here, clearly the value of test statistics is less than the critical value of t as -2.4 < -1.74, so we reject our null hypothesis.
(b) Here, test statistics, t = -1.83 and level of significance is 0.01.
Now, at 0.051 significance level, the t table gives critical value of -2.567 at 17 degree of freedom.
Here, clearly the value of test statistics is more than the critical value of t as -2.567 < -1.83, so we fail to reject our null hypothesis.
(c) Here, test statistics, t = 0.57 and level of significance is not given so we assume it to be 0.05.
Now, at 0.05 significance level, the t table gives critical value of -1.74 at 17 degree of freedom.
Here, clearly the value of test statistics is more than the critical value of t as -1.74 < 0.57, so we fail to reject our null hypothesis.