Answer:
The correct option is option (B)
Therefore the air pressure inside the balloon will be double.
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's Law:
At a constant temperature, the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas varies inversely to its volume.
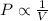
Charles Law:
At a constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas varies directly to its temperature (in kelvin).
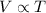
Combination of two laws is
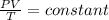
Then,
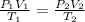
Given that,
The final volume is half of initial volume and the temperature remains constant.
So,
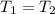 ,
,
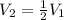
Then,
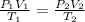
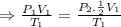
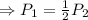
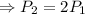
⇒Final Pressure = twice of the initial pressure
Therefore the air pressure inside the balloon will be double.