Answer:
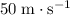 , assuming that the force on the golf ball was constant.
, assuming that the force on the golf ball was constant.
Step-by-step explanation:
Assume that the force the golf club exerted on the golf ball a constant force of magnitude
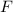 . Let
. Let
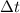 denote the duration the club was in contact with the golf ball. The impulse of this force would be:
denote the duration the club was in contact with the golf ball. The impulse of this force would be:
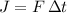 .
.
Let
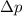 denote the change in the momentum of this golf ball. By the impulse-momentum theorem, this
denote the change in the momentum of this golf ball. By the impulse-momentum theorem, this
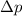 would be equal to the impulse on the golf ball.
would be equal to the impulse on the golf ball.
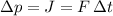 .
.
The momentum
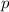 of this golf ball is the scalar product between the mass
of this golf ball is the scalar product between the mass
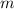 of this golf ball and the velocity
of this golf ball and the velocity
 of this golf ball. The mass of this golf ball stays the same. Thus, when the momentum of this golf ball changes by
of this golf ball. The mass of this golf ball stays the same. Thus, when the momentum of this golf ball changes by
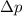 , the velocity of this golf ball would change by
, the velocity of this golf ball would change by
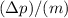 .
.
The change in the velocity of this golf ball would thus be:
 .
.
(Note that
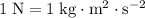 .)
.)