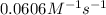Answer : The rate constant at 525 K is,
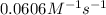
Explanation :
According to the Arrhenius equation,
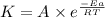
or,
![\log ((K_2)/(K_1))=(Ea)/(2.303* R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/x29hmr496eckje089dimzyhsspavwcfh8n.png)
where,
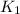 = rate constant at
= rate constant at
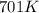 =
=
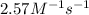
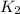 = rate constant at
= rate constant at
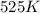 = ?
= ?
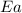 = activation energy for the reaction =
= activation energy for the reaction =
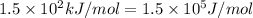
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mole.K
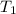 = initial temperature = 701 K
= initial temperature = 701 K
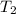 = final temperature = 525 K
= final temperature = 525 K
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get:
![\log ((K_2)/(2.57M^(-1)s^(-1)))=(1.5* 10^5J/mol)/(2.303* 8.314J/mole.K)[(1)/(701K)-(1)/(525K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/754lfn4dwauwg63h378oa4lkalezn8oyrd.png)
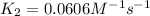
Therefore, the rate constant at 525 K is,