Answer:
The partial pressure of
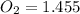 bar.
bar.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Volume
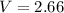 L
L
Total pressure
 bar
bar
Temperature of system
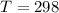 K
K
Moles of nitrogen
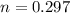 mole
mole
Partial pressure
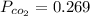 bar
bar
From ideal gas equation,
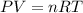
Where
 = gas constant
= gas constant
First finding partial pressure of nitrogen
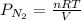
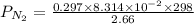
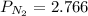 bar
bar
We know, total pressure is given by
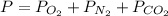
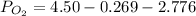
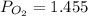 bar
bar
Therefore, the partial pressure of
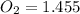 bar.
bar.