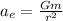Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We assume that:
M to represent the mass of the earth
m to equally represent the mass of the moon
r should be the distance between the center of the earth to the center of the moon.
Then;
the expression for the gravitational force can be written as:
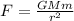
Where
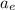 is the acceleration produced by the earth; then:
is the acceleration produced by the earth; then:
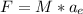
Then:
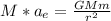
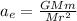
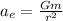
Therefore, the magnitude of the acceleration of the earth due to the gravitational pull of the moon