Answer:
The final concentration is 2 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Dilution is the procedure to prepare a less concentrated solution from a more concentrated one. It consists of adding more solvent.
The amount of solute (the solute is the solid, liquid or gaseous substance that dissolves in the solvent to produce a homogeneous mixture known as a solution and is generally found in a smaller proportion) does not vary. The volume of the solvent varies, so that the concentration of the solute decreases, as the volume of the solution increases.
In summary, dilution is a procedure by which the concentration of a solution is decreased, generally with the addition of a diluent.
One way to calculate concentrations or volumes in dilutions is through the expression:
Ci * Vi = Cf * Vf
where
- Ci = initial concentration
- Vi = Initial volume
- Cf = Final concentration
- Vf = Final volume
In this case:
- Ci= 6 M
- Vi= 100 mL= 0.1 L (1 L=1000 mL)
- Cf= ?
- Vf= 300 mL= 0.3 L
Replacing:
6 M* 0.1 L= Cf*0.3 L
Solving:
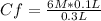
Cf=2 M
The final concentration is 2 M