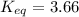Answer:
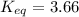
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium constant, Ke, at certain temperature, T, and the standard free energy of formation (ΔG°f) are related by the equation:
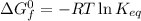
From which you can obtain:
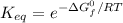
Substituting ΔG°f = 82.4kJ/mol, T = 25 + 273.15 K = 298.15 K and R = 0.008314 kJ·mol⁻¹ K⁻¹:
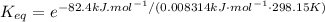
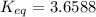
Rounding to three significant figures: