13.5 is the new concentration of this solution if it is boiled down to a
volume of 1.0 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
Data given:
Initial volume of the solution of sea water = 2.5 litre
Molarity of NaCl solution M1 = 5.4 M
fInal volume = 1 litre
final molarity = ?
Assuming that no loss of NaCl from sea water took place when the sea water was boiled.
applying the formula for change in concentration as:
Minitial V initial = Mfinal X Vfinal
M final =
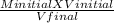
Putting the values in the equation:
Mfinal =
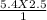
M final = 13.5 M
thus it can be concluded that molarity will increase drastically when volume gets reduced from 2.5 litre to 1 litre. The solution becomes highly concentrated as water volume decreases due to evaporation.