Answer:
13.
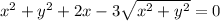
14.
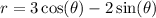
Explanation:
Question 13
Conversion from Polar equation to rectangular equation:
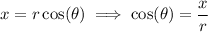
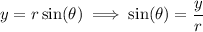
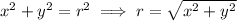
Given:
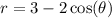
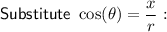
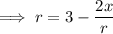
Multiply both sides by r:
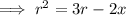
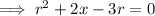
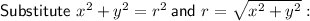
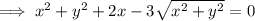
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 14
Conversion from Rectangular equation to polar equation:
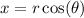
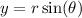
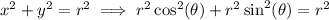
Given:
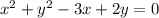
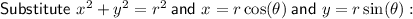
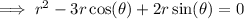
Factor out common term r:
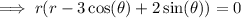
Divide both sides by r:
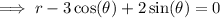
Rewrite to make r the subject: