The answer for the following problem is mentioned below.
- Therefore the final moles of the gas is 14.2 ×
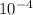 moles.
moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Initial volume (
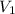 ) = 230 ml
) = 230 ml
Final volume (
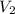 ) = 860 ml
) = 860 ml
Initial moles (
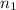 ) = 3.8 ×
) = 3.8 ×
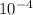 moles
moles
To find:
Final moles (
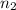 )
)
We know;
According to the ideal gas equation;
P × V = n × R × T
where;
P represents the pressure of the gas
V represents the volume of the gas
n represents the no of the moles of the gas
R represents the universal gas constant
T represents the temperature of the gas
So;
V ∝ n
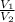 =
=
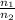
where,
(
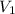 ) represents the initial volume of the gas
) represents the initial volume of the gas
(
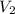 ) represents the final volume of the gas
) represents the final volume of the gas
(
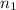 ) represents the initial moles of the gas
) represents the initial moles of the gas
(
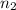 ) represents the final moles of the gas
) represents the final moles of the gas
Substituting the above values;
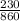 =
=
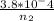
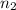 = 14.2 ×
= 14.2 ×
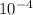 moles
moles
Therefore the final moles of the gas is 14.2 ×
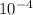 moles.
moles.