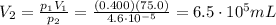c) 29.8 mL
d) 5375 mL
e)
Step-by-step explanation:
c)
We can solve this problem by using Boyle's Law, which states that:
"For a fixed mass of an ideal gas kept at constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to its volume"
Mathematically:
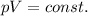
where
p is the pressure of the gas
V is its volume
We can rewrite the formula as
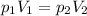
For the gas in this problem:
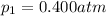 is the initial pressure
is the initial pressure
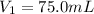 is the initial volume
is the initial volume
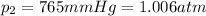 is the final pressure (using the conversion factor
is the final pressure (using the conversion factor
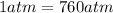 )
)
Solving for V2, we find the final volume:
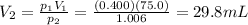
d)
We can solve this part by using again the equation:
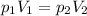
Where in this case we have:
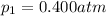 is the initial pressure
is the initial pressure
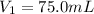 is the initial volume
is the initial volume
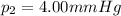 is the final pressure
is the final pressure
Converting into atmospheres,
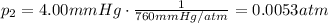
And solving for V2, we find the final volume:
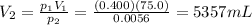
e)
As before, we use Boyles' Law:
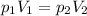
In this part we have:
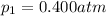 is the initial pressure of the gas
is the initial pressure of the gas
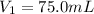 is the initial volume of the gas
is the initial volume of the gas
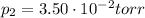
1 torr is equivalent to 1 mmHg, so the conversion factor is the same as before, therefore the final pressure in atmospheres is:
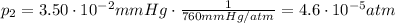
And so, the final volume of the krypton gas is: