Answer:
The new volume of the gas is 73.31 mL at -16°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's Law:
The pressure of a given mass at a constant temperature of an ideal gas is inversely proportion to its volume.
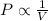
Charles' Law:
The volume is directly proportional to the temperature of an ideal gas of a given mass at a constant pressure.
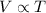
Combined two gas laws
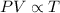
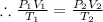
Given that,
A sample of neon gas closed vessel occupied 85.0 mL at 25.0°C with constant P and n.
Here
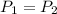 ,
,
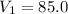 mL,
mL,
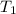 =( 25+273)K=298 k
=( 25+273)K=298 k
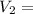 ? ,
? ,
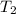 =(-16+273)K=257 k
=(-16+273)K=257 k
Since the pressure is constant.
So, the gas equation becomes
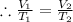
Putting the value of
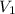 ,
,
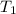 and
and
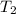
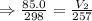
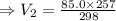
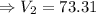 mL
mL
The new volume of the gas is 73.31 mL at -16°C.