Given question is incomplete. The complete question is as follows.
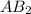 is a molecule that reacts readily with water. Calculate the bond energy of the A–B bond using the standard enthalpy of reaction and the bond energy data provided. Enter a number in kJ to 0 decimal places.
is a molecule that reacts readily with water. Calculate the bond energy of the A–B bond using the standard enthalpy of reaction and the bond energy data provided. Enter a number in kJ to 0 decimal places.
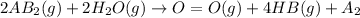
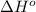 = –142 kJ
= –142 kJ
Bond: O–H O=O H–B
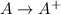
Bond energy (kJ/mol): 467 498 450 321
Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is as follows.
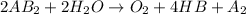
Now, we will calculate the enthalpy of reaction as follows.
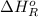 = -142 kJ
= -142 kJ
Also, we know that
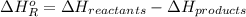
=
![[(2 * 2 (A-B) + 2 * 2 (O-H)] - [(O=O) + 4(H-B) + (A-A)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o0cxzsplhi3oriv63vntjsiimnuaaszuc1.png)
-142 =
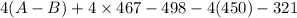
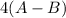 = -142 - 1868 + 498 + 1800 + 321
= -142 - 1868 + 498 + 1800 + 321
= 609
(A-B) = 152.25 kJ/mol
Thus, we can conclude that the bond energy of the A–B bond is 152.25 kJ/mol.