Answer:
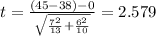
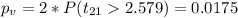
Comparing the p value with the significance level
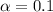 we see that
we see that
 so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, and the difference between the two mean sales per month for the 2 flavors is significantly different.
so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, and the difference between the two mean sales per month for the 2 flavors is significantly different.
Explanation:
Previous concepts
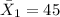 represent the mean for sample 1
represent the mean for sample 1
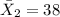 represent the mean for sample 2
represent the mean for sample 2
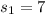 represent the sample standard deviation for 1
represent the sample standard deviation for 1
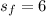 represent the sample standard deviation for 2
represent the sample standard deviation for 2
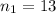 sample size for the group 2
sample size for the group 2
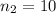 sample size for the group 2
sample size for the group 2
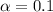 Significance level provided
Significance level provided
t would represent the statistic (variable of interest)
Concepts and formulas to use
We need to conduct a hypothesis in order to check if the difference in the population means, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
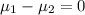
Alternative hypothesis:
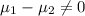
We don't have the population standard deviation's, so for this case is better apply a t test to compare means, and the statistic is given by:
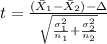 (1)
(1)
And the degrees of freedom are given by
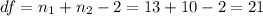
t-test: Is used to compare group means. Is one of the most common tests and is used to determine whether the means of two groups are equal to each other.
With the info given we can replace in formula (1) like this:
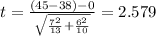
P value
Since is a bilateral test the p value would be:
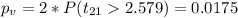
Comparing the p value with the significance level
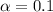 we see that
we see that
 so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, and the difference between the two mean sales per month for the 2 flavors is significantly different.
so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, and the difference between the two mean sales per month for the 2 flavors is significantly different.