Answer:
The distance between first-order and second-order bright fringes is 12.66mm.
Step-by-step explanation:
The physicist Thomas Young establishes through its double slit experiment a relationship between the interference (constructive or destructive) of a wave, the separation between the slits, the distance between the two slits to the screen and the wavelength.
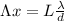 (1)
(1)
Where
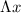 is the distance between two adjacent maxima, L is the distance of the screen from the slits,
is the distance between two adjacent maxima, L is the distance of the screen from the slits,
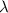 is the wavelength and d is the separation between the slits.
is the wavelength and d is the separation between the slits.
The values for this particular case are:
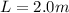
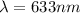
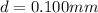
Notice that is necessary to express L and
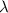 in units of milimeters.
in units of milimeters.
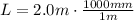 ⇒
⇒
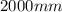
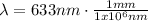 ⇒
⇒
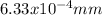
Finally, equation 1 can be used:
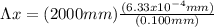
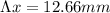
Hence, the distance between first-order and second-order bright fringes is 12.66mm.