Answer:
Null Hypothesis,
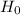 :
:
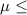 14 automobiles per month
14 automobiles per month
Alternate Hypothesis,
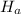 :
:
 > 14 automobiles per month
> 14 automobiles per month
Explanation:
We are given that the manager of an automobile dealership is considering a new bonus plan designed to increase sales volume. Currently, the mean sales volume is 14 automobiles per month.
The manager wants to conduct a research study to see whether the new bonus plan increases sales volume.
Let
 = population mean sales volume after the new bonus plan
= population mean sales volume after the new bonus plan
So, Null Hypothesis,
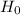 :
:
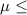 14 automobiles per month
14 automobiles per month
Alternate Hypothesis,
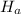 :
:
 > 14 automobiles per month
> 14 automobiles per month
Here, null hypothesis states that the new bonus plan does not increase the sales volume as the sales is less than or equal to 14 automobiles per month.
And alternate hypothesis states that the new bonus plan increases the sales volume as the sales is more than 14 automobiles per month.
Now, conclusion on when the null hypothesis (
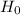 ) can be rejected and when it cannot be rejected is based on two perspectives;
) can be rejected and when it cannot be rejected is based on two perspectives;
- From test statistics point of view;
- If the test statistics is more than the critical value of any respective distribution, then we will reject our null hypothesis.
- If the test statistics is less than the critical value of any respective distribution, then we cannot reject our null hypothesis.
2. From P-value point of view;
- If the p-value of the test statistics is more than level of significance (
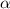 ), then we will not reject our null hypothesis.
), then we will not reject our null hypothesis.
- If the p-value of the test statistics is less than level of significance (
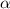 ), then we will reject our null hypothesis.
), then we will reject our null hypothesis.