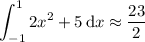Split the integration interval [-1, 1] into 4 subintervals:
[-1, -1/2], [-1/2, 0], [0, 1/2], [1/2, 1]
Each subinterval has a length of 1/2, which acts as the height of the corresponding trapezoid over the subinterval. The "bases" of the trapezoid are the function's values at the endpoint of the subinterval. For instance, over the first subinterval, we have
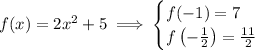
So over this subinterval, the trapezoid contributes an area of
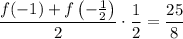
Do the same with the other 3 trapezoids; you'll find