Answer:
56.25 N
Step-by-step explanation:
Given,
Radius of the planet, r = 1000 km
Gravitational force, F = 100 N
Initial distance from the planet, d = 500 km
Final distance from the planet, D = 1000 km
Lets assume, mass of planet = M
mass of the object = m.
As per the gravitational law, the force due to gravity is given as
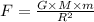
where, G = gravitational constant
R = distance between the two objects.
Case 1: when the object is at a distance of 500 km from the planet,
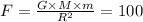
Here, R = 1000 + 500 = 1500 km, so
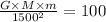
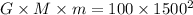
Case 2: when the object is at a distance of 1000 km from the planet, so
now, R = 1000 + 1000 = 2000 km
Now the gravitational force, F' will be
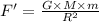
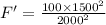
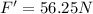
Thus, the gravitational force will now be reduced to 56.25 N.