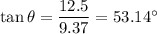Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of the car, m = 1500 kg
Initial speed of the car, u = 25 m/s east
Mass of the van, m' = 2500 kg
Initial speed of van, u' = 20 m/s north
It is assumed that the vehicles undergo a perfectly inelastic collision. The law of conservation of linear momentum gives the velocity after the collision as :
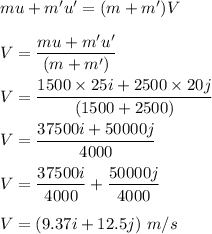
Magnitude of velocity,
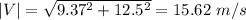
Direction,