The given question is incomplete. The complete question is:
Determine the acid dissociation constant for a 0.10 M acetic acid solution that has a pH of 2.87. Acetic acid is a weak monoprotic acid and the equilibrium equation of interest is
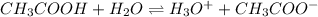
Answer: 0.000017
Step-by-step explanation:
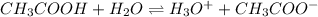
cM 0 M 0 M

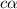
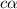
So dissociation constant will be:
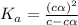
Give c= 0.10 M and
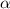 = dissociation constant = ?
= dissociation constant = ?
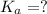
Putting in the values we get:
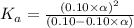
![pH=-log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wyj0nahkywle04sx44478osqilvygxax2t.png)
![2.87=-log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/mf5nhzxxjvya5hg4v1el3mvlod5kvvunbp.png)
![[H^+]=1.35* 10^(-3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ar3a2g95s9enfsu178x0jptdj7xjb6nn2v.png)
![[H^+]=c* \alpha](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6iel1ors69hl9ilvy1vx41nw46k5uyhjc0.png)
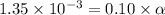
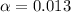
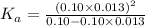
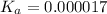
Thus the acid dissociation constant is 0.000017