Answer:
The magnitude of the average force of friction acting on the ice skater while she slows to a stop is 15.65 N
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
mass of the ice skater, m = 52.5 kg
speed of the ice skater, u = 2.25 m/s
time for her gliding, t = 7.55 s
To determine the magnitude of the average force of friction acting on the ice skater while she slows to a stop, we apply Newton's second law of motion;
F = ma
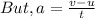
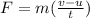
where;
F is average force of friction acting on the ice skater
v is the final speed speed of the ice skater = 0
u is the initial speed of the ice skater
t is time
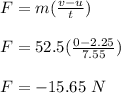
Thus, the magnitude of the average force of friction acting on the ice skater while she slows to a stop is 15.65 N