Answer: 3026.5 J
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
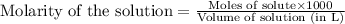 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of
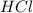 solution = 2.112 M
solution = 2.112 M
Volume of solution = 25.00 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
a)
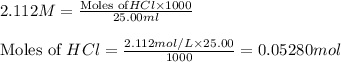
The balanced chemical reaction is:

As
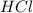 is the limiting reagent , it limits the formation of product.
is the limiting reagent , it limits the formation of product.
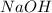 is the excess reagent.
is the excess reagent.
1 mole of HCl produces = 1 mole of
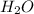
0.05280 mole of HCl produces =
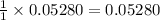 moles of
moles of
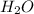
Given :
Energy released when 1 mole of
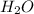 is produced = 57320 J
is produced = 57320 J
Thus Energy released when 0.05280 moles of
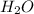 is produced =
is produced =
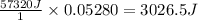
Thus 3026.5 J is the total theoretical heat released