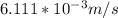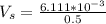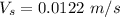Answer:
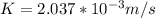
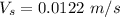
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that;
diameter (d) = 10cm/2 = 0.1m/2 = 0.05 m
length (l) = 10 cm = 0.1 m
porosity = 50%
height (h) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
time (t) = 5 s
volume (v) = 60 cm³ = 60 × 10⁻⁶ m³
Q (flow rate) =
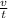
Q =
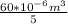
Q =
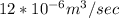
From constant head method, we use the relation K =
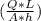 to determine the hydraulic conductivity ; we have:
to determine the hydraulic conductivity ; we have:
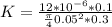
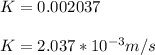
Seepage velocity
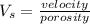
where; velocity =
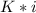
=
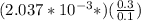
=