Answer: 14.62 ml
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of the solution.
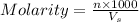
where,
n= moles of solute
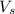 = volume of solution in ml = 250 ml
= volume of solution in ml = 250 ml
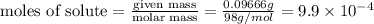
Now put all the given values in the formula of molarity, we get
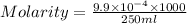
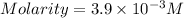
To calculate the volume of base, we use the equation given by neutralization reaction:
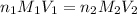
where,
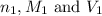 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of acid which is
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of acid which is
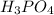
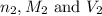 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base which is NaOH.
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base which is NaOH.
We are given:
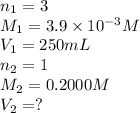
Putting values in above equation, we get:
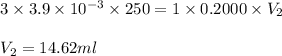
Thus the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point is 14.62 ml