Answer:
76.10% probability that between 19 and 28 circuits in the sample are defective
Explanation:
I am going to use the binomial approximation to the normal to solve this question.
Binomial probability distribution
Probability of exactly x sucesses on n repeated trials, with p probability.
Can be approximated to a normal distribution, using the expected value and the standard deviation.
The expected value of the binomial distribution is:
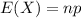
The standard deviation of the binomial distribution is:
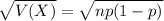
Normal probability distribution
Problems of normally distributed samples can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
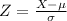
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
When we are approximating a binomial distribution to a normal one, we have that
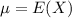 ,
,
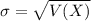 .
.
In this problem, we have that:
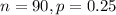
So
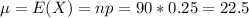
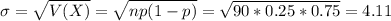
P(19 ≤ X ≤ 28)
Using continuity correction, this is
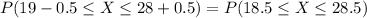 , which is the pvalue of Z when X = 28.5 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 18.5. So
, which is the pvalue of Z when X = 28.5 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 18.5. So
X = 28.5
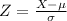
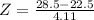
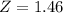
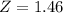 has a pvalue of 0.9279
has a pvalue of 0.9279
X = 18.5
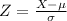
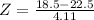

 has a pvalue of 0.1669
has a pvalue of 0.1669
0.9279 - 0.1669 = 0.7610
76.10% probability that between 19 and 28 circuits in the sample are defective