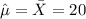Answer:
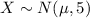
Where
 and
and
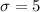
For this case we select a sample of n =49 observations and we got a sample mean os :
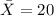
From the definition of mean we have that :
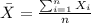
And if we find the expected value of this estimator we got this:
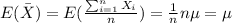
So then the best estimator unbiased for the population mean is the sample mean:
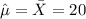
Explanation:
Previous concepts
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
Solution to the problem
Let X the random variable that represent the weekly spending of a population, and for this case we know the distribution for X is given by:
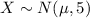
Where
 and
and
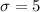
For this case we select a sample of n =49 observations and we got a sample mean os :
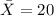
From the definition of mean we have that :
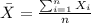
And if we find the expected value of this estimator we got this:
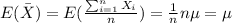
So then the best estimator unbiased for the population mean is the sample mean: