Answer & Explanation:
(a)
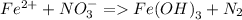
reducing agent = Fe²⁺
Oxidizing agent = NO₃⁻
oxidation
Fe²⁺ ⇒ Fe(OH)₃
reduction
NO₃⁻ ⇒ N₂
Oxidation Half Reaction
(redox reactions are balanced by adding appropriate H⁺ and H₂O atoms)
Fe²⁺ ⇒ Fe(OH)₃
Balance O atoms
Fe²⁺ + 3H₂O ⇒ Fe(OH)₃
Balance H atoms
Fe² + 3H₂0 ⇒ Fe(OH)₃ + 3H⁺
balance Charge
Fe² + 3H₂0 ⇒ Fe(OH)₃ + 3H⁺ + e⁻..............(1)
reduction Half Reaction
NO₃⁻ ⇒ N₂
Balance N atoms
2NO₃⁻ ⇒N₂
Balance O atoms by adding appropriate H₂O
2NO₃⁻ ⇒ N₂ + 6H₂O
Balance H atoms
2NO₃⁻ + 12H⁺ ⇒ N₂ + 6H₂O
Balance Charge
2NO₃⁻ + 12H⁺ + 10e⁻⇒ N₂ + 6H₂O.................(2)
Combine Equation (1) and (2)
(1) × 10: 10Fe² + 30H₂0 ⇒ 10Fe(OH)₃ + 30H⁺ + 10e⁻
(2) × 1: 2NO₃⁻ + 12H⁺ + 10e⁻⇒ N₂ + 6H₂O
(1) + (2): 10Fe² + 30H₂0 + 2NO₃⁻ + 12H⁺ + 10e⁻ ⇒10Fe(OH)₃ + 30H⁺ + 10e⁻ +
N₂ + 6H₂O
10Fe² + 24H₂0 + 2NO₃⁻ ⇒ 10Fe(OH)₃ + 18H⁺ + N₂
this is the balanced reaction
REDUCTION POTENTIAL
10Fe²⁺(aq) + 10e⁻ ⇒ 10Fe(OH)₃(aq) E°ox = 10(-0.44) = -4.4V
2NO₃⁻(aq) - 2e⁻ ⇌ N₂(g) + 18H⁺ E°red = 2(+0.80) = +1.6
10Fe² + 24H₂0 + 2NO₃⁻ ⇒ 10Fe(OH)₃ + 18H⁺ + N₂ E°cell = -2.8V
E°cell = E°red + E°ox